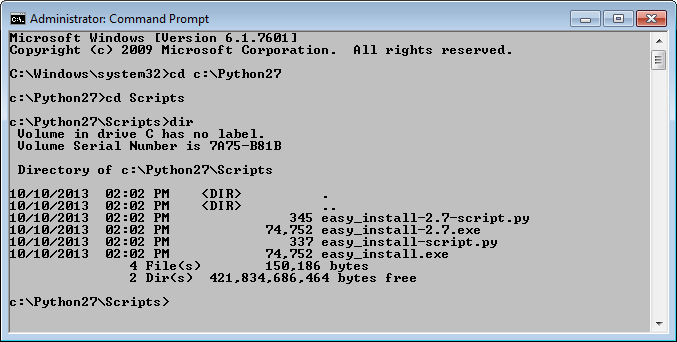
Change directory to where you installed Python, and then change directory to the Scripts subdirectory.
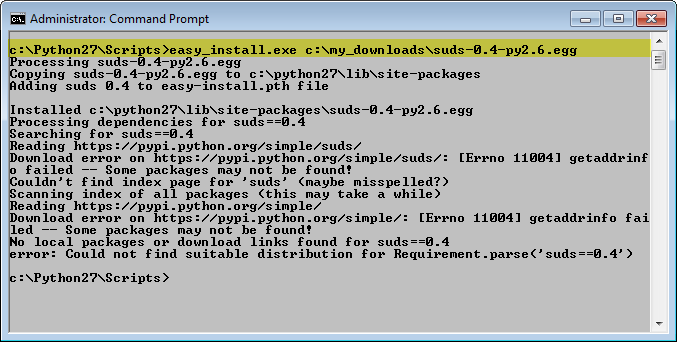
To install SUDS, run the easy_install.exe program and point it to the suds egg that you download.
This tutorial provides step-by-step instructions for installing a Python 2.x, suds/SOAP environment and using it to log in to the Verizon ThingSpace Platform and make a request using the Wireless Network Services API. The content in this application note is not intended to cover all aspects of Python, Python programming, SOAP or XML usage. It only describes the basic procedure for accomplishing a typical ThingSpace Platform function. It does not provide Python language training. No support is provided for this tutorial or Python.
The task described in this application note was written with the following versions of software. It may or may not work with other versions or operating systems.
The following terms apply to the task described in this application note:
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Asynchronous Response | A delayed response to a web service request. All Wireless Network Services API methods provide synchronous responses, which are immediate. Certain Wireless Network Services API methods provide asynchronous responses as well, such as those in the Carrier Service, where responses may be delayed because of transaction processing time. When you initiate a Wireless Network Services request that has an asynchronous response, the initial synchronous response contains a Request ID that identifies the request. The complete response to the request is returned later, after the asynchronous operation has completed. The asynchronous response is sent to your callback listening service. You can match the asynchronous response with your original request using the Request ID. |
| Callback Listening Service | A service that:
Responses to certain Wireless Network Services API requests, such as those in the Carrier Service, may be delayed due to transaction processing time, and are known as asynchronous responses. The Callback Listening Service receives these asynchronous responses. There are several tutorials on how to create a callback listening service:
After you have created a callback listening service, you must register it with the ThingSpace Platform so that you receive the right type of callback messages at the right URL. The Callback Registration Service page contains additional information about registration. |
Before performing any task in this application note, you must sign up for the Verizon ThingSpace Platform Services and download the SDK.
NOTE: There isn't a good SOAP module for Python version 3.x yet, so it's easier to use 2.7.x for SOAP projects.
Suds is a SOAP module for Python, which allows Python to consume wsdl files.
Setuptools that you installed in the previous step includes an Easy Install program that you can use to install the correct version of suds.
Change directory to where you installed Python, and then change directory to the Scripts subdirectory.

To install SUDS, run the easy_install.exe program and point it to the suds egg that you download.

Python is now ready to talk to SOAP applications.
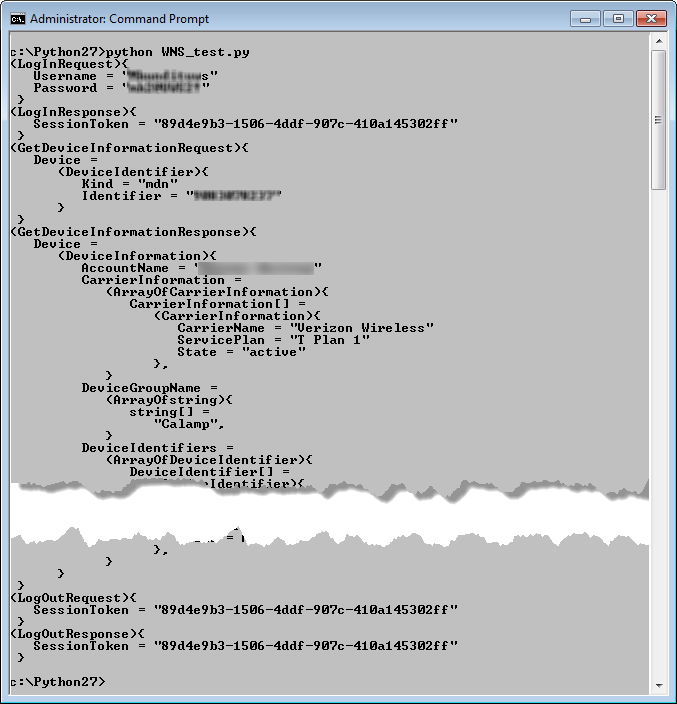
This test script will log in to the Verizon ThingSpace Platform and retrieve information for a single device. Copy the following code segment (highlighted in gray) into your favorite text editor (such as Notepad):
"""This script will log in to web services, print the session token, retrieve the device
list for one device, log out and print the logout token."""
from suds.client import Client
from suds.sax.element import Element
account = 'your_account_name'
username = 'your_username'
password = 'your_password'
phonenumber = 'the_mdn_of_the_line_of_service'
# create the session service
session_wsdl='file:///path_to_SDK/SessionService/SessionService.wsdl'
session = Client(session_wsdl)
# log in to the ThingSpace Platform
login_req = session.factory.create('ns1:LogInRequest')
login_resp = session.factory.create('ns1:LogInResponse')
login_req.Username = username
login_req.Password = password
print login_req
login_resp = session.service.LogIn(login_req)
print login_resp
# create a soap header element to hold the session token
token_element = Element('token')
token_element.setText('{}'.format(login_resp.SessionToken))
token_element.attributes.append('xmlns="http://nphase.com/unifiedwebservice/v2"')
session.set_options(soapheaders=token_element)
# create the device service
device_wsdl='file:///path_to_SDK/DeviceService/DeviceService.wsdl'
device = Client(device_wsdl)
device.set_options(soapheaders=token_element)
# request information about a specific device on the account
device_info_req = device.factory.create('ns2:GetDeviceInformationRequest')
device_info_resp = device.factory.create('ns2:GetDeviceInformationResponse')
device_info_req.Device.Kind = 'mdn'
device_info_req.Device.Identifier = phonenumber
print device_info_req
device_info_resp = device.service.GetDeviceInformation(device_info_req)
print device_info_resp
# log out of the API service
logout_req = session.factory.create('ns1:LogOutRequest')
logout_resp = session.factory.create('ns1:LogOutResponse')
logout_req.SessionToken = login_resp.SessionToken
print logout_req
logout_resp = session.service.LogOut(logout_req)
print logout_resp
Replace the bold sections of the following lines in the code with the appropriate values. Be sure to leave the single quotes.
Run the file with the python command, as shown below: